- 電子メール : David@tmaxcn.com
- 電子メール : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
ブログ
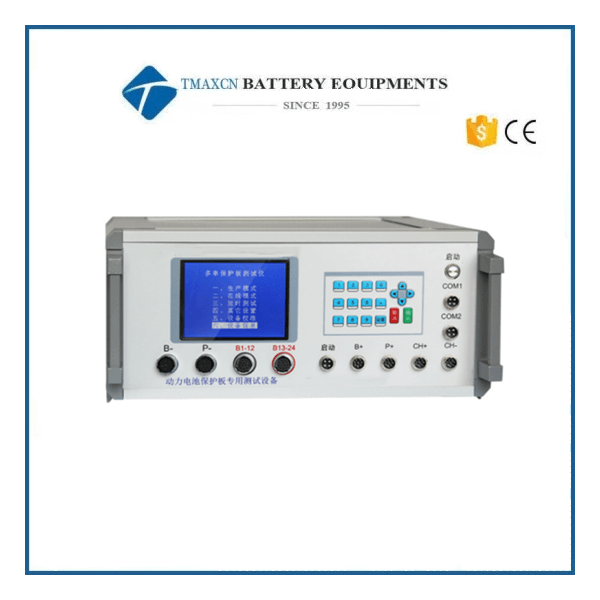
BMS Tester
A BMS (Battery Management System) tester is a specialized piece of equipment designed to evaluate, validate, and calibrate the performance of battery management systems. The BMS is a critical component in modern battery systems, responsible for monitoring key parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, state of charge (SOC), and state of health (SOH). A reliable BMS ensures the safe, efficient, and optimal operation of batteries, particularly in applications like electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and consumer electronics.
In this article, we will explore the types, functionalities, advantages, challenges, and innovations driving the evolution of BMS testers.
●Types of BMS Testers
BMS testers can be categorized based on their application and functionality:
1. Functional Testers
Purpose: Verify that the BMS operates correctly under normal conditions.
Key Features:
Simulate realworld battery conditions (e.g., charging/discharging cycles).
Test basic functions like voltage, current, and temperature monitoring.
2. Performance Testers
Purpose: Assess the accuracy and precision of the BMS in measuring and managing battery parameters.
Key Features:
Evaluate SOC and SOH estimation algorithms.
Test balancing capabilities for multicell battery packs.
3. Safety Testers
Purpose: Ensure the BMS can handle fault conditions and protect the battery from damage.
Key Features:
Simulate overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, and overheating scenarios.
Test protection mechanisms like cutoff switches and thermal management systems.
4. Protocol and Communication Testers
Purpose: Validate the communication protocols used by the BMS to interact with other systems.
Key Features:
Test CAN bus, LIN bus, or other communication interfaces.
Ensure data integrity and synchronization between the BMS and external controllers.
5. EndofLine Testers
Purpose: Conduct final quality checks before shipping the BMS to customers.
Key Features:
Perform comprehensive tests covering all aspects of BMS functionality.
Generate detailed reports for compliance and traceability.
●Functionalities of a BMS Tester
1. Parameter Simulation:
Simulates various operating conditions (e.g., voltage, current, temperature) to test the BMS's response.
2. Data Logging:
Records and analyzes data from the BMS during testing for further evaluation.
3. Fault Injection:
Introduces simulated faults to verify the BMS's ability to detect and respond appropriately.
4. Calibration:
Adjusts the BMS settings to ensure accurate measurements and optimal performance.
5. Communication Testing:
Validates the BMS's ability to communicate effectively with external systems using standard protocols.
●Advantages of BMS Testers
1. Improved Reliability:
Ensures the BMS performs consistently and accurately under all conditions.
2. Enhanced Safety:
Verifies that the BMS can protect the battery and surrounding systems from damage.
3. Cost Savings:
Identifies defects early in the development process, reducing the cost of repairs or recalls.
4. Compliance Assurance:
Ensures the BMS meets industry standards and regulations.
5. Customization:
Can be tailored to specific battery chemistries, sizes, and applications.
●Challenges in BMS Testing
1. Complexity:
Modern BMS designs involve sophisticated algorithms and multiple communication protocols, making testing challenging.
2. Dynamic Conditions:
Simulating realworld operating conditions, especially extreme scenarios, requires advanced equipment.
3. Interoperability:
Ensuring compatibility with various battery chemistries and external systems can be difficult.
4. TimeConsuming:
Comprehensive testing can be timeintensive, potentially slowing down production schedules.
5. High Costs:
Advanced BMS testers often come with significant upfront investment.
●Innovations in BMS Testers
To address these challenges and enhance testing capabilities, manufacturers are incorporating cuttingedge technologies:
1. AI and Machine Learning:
Predictive analytics optimize test sequences, identify potential issues, and improve overall efficiency.
2. RealTime Monitoring:
Integrated sensors and data analytics tools provide continuous feedback during testing.
3. Modular Design:
Flexible systems allow for easy reconfiguration to accommodate different battery types and applications.
4. Virtual Testing:
Simulated environments enable testing of BMS algorithms without physical hardware.
5. IoT Integration:
Connectivity with cloudbased platforms allows remote monitoring and analysis of test results.
●Applications of BMS Testers
BMS testers are used in various industries and applications, including:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Ensures the BMS in EVs can handle highpower demands and varying environmental conditions.
2. Renewable Energy Storage:
Validates the BMS's ability to manage largescale battery systems for grid storage.
3. Consumer Electronics:
Tests BMS performance in portable devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearables.
4. Industrial Equipment:
Ensures the reliability of BMS in heavyduty applications like trucks, buses, and construction machinery.
●The Future of BMS Testers
As battery technology continues to evolve, so too will the tools used to test and validate BMS systems. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous testing systems will reduce human intervention and improve consistency.
2. Customization Options:
Modular designs will allow testers to adapt to emerging battery technologies and chemistries.
3. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and recycling capabilities will become integral parts of future systems.
4. Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Solidstate batteries, wireless charging, and autonomous systems will drive new innovations in testing methodologies.
5. Smart Testing Platforms:
IoTenabled systems will leverage big data and AI to optimize testing processes, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency.
●Conclusion
BMS testers play a vital role in ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of battery management systems. Their ability to simulate realworld conditions, detect faults, and validate communication protocols makes them indispensable in the development and production of modern battery systems.
October 21,2025.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
A BMS (Battery Management System) tester is a specialized piece of equipment designed to evaluate, validate, and calibrate the performance of battery management systems. The BMS is a critical component in modern battery systems, responsible for monitoring key parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, state of charge (SOC), and state of health (SOH). A reliable BMS ensures the safe, efficient, and optimal operation of batteries, particularly in applications like electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and consumer electronics.
In this article, we will explore the types, functionalities, advantages, challenges, and innovations driving the evolution of BMS testers.
●Types of BMS Testers
BMS testers can be categorized based on their application and functionality:
1. Functional Testers
Purpose: Verify that the BMS operates correctly under normal conditions.
Key Features:
Simulate realworld battery conditions (e.g., charging/discharging cycles).
Test basic functions like voltage, current, and temperature monitoring.
2. Performance Testers
Purpose: Assess the accuracy and precision of the BMS in measuring and managing battery parameters.
Key Features:
Evaluate SOC and SOH estimation algorithms.
Test balancing capabilities for multicell battery packs.
3. Safety Testers
Purpose: Ensure the BMS can handle fault conditions and protect the battery from damage.
Key Features:
Simulate overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, and overheating scenarios.
Test protection mechanisms like cutoff switches and thermal management systems.
4. Protocol and Communication Testers
Purpose: Validate the communication protocols used by the BMS to interact with other systems.
Key Features:
Test CAN bus, LIN bus, or other communication interfaces.
Ensure data integrity and synchronization between the BMS and external controllers.
5. EndofLine Testers
Purpose: Conduct final quality checks before shipping the BMS to customers.
Key Features:
Perform comprehensive tests covering all aspects of BMS functionality.
Generate detailed reports for compliance and traceability.
●Functionalities of a BMS Tester
1. Parameter Simulation:
Simulates various operating conditions (e.g., voltage, current, temperature) to test the BMS's response.
2. Data Logging:
Records and analyzes data from the BMS during testing for further evaluation.
3. Fault Injection:
Introduces simulated faults to verify the BMS's ability to detect and respond appropriately.
4. Calibration:
Adjusts the BMS settings to ensure accurate measurements and optimal performance.
5. Communication Testing:
Validates the BMS's ability to communicate effectively with external systems using standard protocols.
●Advantages of BMS Testers
1. Improved Reliability:
Ensures the BMS performs consistently and accurately under all conditions.
2. Enhanced Safety:
Verifies that the BMS can protect the battery and surrounding systems from damage.
3. Cost Savings:
Identifies defects early in the development process, reducing the cost of repairs or recalls.
4. Compliance Assurance:
Ensures the BMS meets industry standards and regulations.
5. Customization:
Can be tailored to specific battery chemistries, sizes, and applications.
●Challenges in BMS Testing
1. Complexity:
Modern BMS designs involve sophisticated algorithms and multiple communication protocols, making testing challenging.
2. Dynamic Conditions:
Simulating realworld operating conditions, especially extreme scenarios, requires advanced equipment.
3. Interoperability:
Ensuring compatibility with various battery chemistries and external systems can be difficult.
4. TimeConsuming:
Comprehensive testing can be timeintensive, potentially slowing down production schedules.
5. High Costs:
Advanced BMS testers often come with significant upfront investment.
●Innovations in BMS Testers
To address these challenges and enhance testing capabilities, manufacturers are incorporating cuttingedge technologies:
1. AI and Machine Learning:
Predictive analytics optimize test sequences, identify potential issues, and improve overall efficiency.
2. RealTime Monitoring:
Integrated sensors and data analytics tools provide continuous feedback during testing.
3. Modular Design:
Flexible systems allow for easy reconfiguration to accommodate different battery types and applications.
4. Virtual Testing:
Simulated environments enable testing of BMS algorithms without physical hardware.
5. IoT Integration:
Connectivity with cloudbased platforms allows remote monitoring and analysis of test results.
●Applications of BMS Testers
BMS testers are used in various industries and applications, including:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Ensures the BMS in EVs can handle highpower demands and varying environmental conditions.
2. Renewable Energy Storage:
Validates the BMS's ability to manage largescale battery systems for grid storage.
3. Consumer Electronics:
Tests BMS performance in portable devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearables.
4. Industrial Equipment:
Ensures the reliability of BMS in heavyduty applications like trucks, buses, and construction machinery.
●The Future of BMS Testers
As battery technology continues to evolve, so too will the tools used to test and validate BMS systems. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous testing systems will reduce human intervention and improve consistency.
2. Customization Options:
Modular designs will allow testers to adapt to emerging battery technologies and chemistries.
3. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and recycling capabilities will become integral parts of future systems.
4. Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Solidstate batteries, wireless charging, and autonomous systems will drive new innovations in testing methodologies.
5. Smart Testing Platforms:
IoTenabled systems will leverage big data and AI to optimize testing processes, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency.
●Conclusion
BMS testers play a vital role in ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of battery management systems. Their ability to simulate realworld conditions, detect faults, and validate communication protocols makes them indispensable in the development and production of modern battery systems.
What excites you most about the role of BMS testers in advancing battery technology? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these tools can shape the future of energy storage and management.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

